Everything you need to know about Computer Hardware
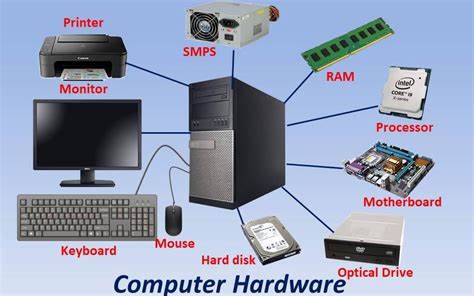
Computer hardware is the collection of physical parts that make a computer system.
A computer can be equipped with various types of Computer Hardware, both internally installed and externally connected.
Computer hardware may sometimes be seen abbreviated as computer hardware.
The Computer Hardware
A computer is made up of many parts:
- Input/output (I/O) devices – These allow you to send information to the
computer or get information from the computer
- Motherboard – A circuit board that allows the CPU to interact with other
parts of the computer. - Central Processing Unit – CPU or Processor for short. The brain of a
computer. Approximately 1.5 in X 1.5 in. Does all the computation/work for
the computer
- Memory – Although memory is technically any form of electronic storage, it
is used most often to identify fast, temporary forms of storage. Accessing the
hard drive for information takes time. When the information is kept in
memory, the CPU can access it much more quickly.
a. Random Access Memory – RAM. Where information is stored
temporarily when a program is run. Information is automatically
pulled into memory, we cannot control this. RAM is cleared
automatically when the computer is shutdown or rebooted. RAM is
volatile (non-permanent).
(b). Read Only Memory – ROM. More permanent than RAM. Data
stored in these chips is nonvolatile — it is not lost when power is
removed. Data stored in these chips is either unchangeable or requires
a special operation to change. The BIOS(Basic Input/output System) is stored in the CMOS(Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor), readonly memory.
(c). Hard Drive – Where you store information permanently most
frequently. This is also nonvolatile. - Ports – Means of connecting peripheral devices to your computer.
a. Serial Port – Often used to connect a older mice, older external
modems, older digital cameras, etc to the computer. The serial port
has been replaced by USB in most cases. 9-pin connector. Small and
short, often gray in color. Transmits data at 19 Kb/s.
b. Monitor Ports – Used to connect a monitor to the computer.
PCs usually use a VGA (Video Graphics Array) analog connector (also
known as a D-Sub connector) that has 15 pins in three rows. Typically
blue in color.
Because a VGA (analog) connector does not support the use of digital
monitors, the Digital Video Interface (DVI) standard was developed.
LCD monitors work in a digital mode and support the DVI format. At one
time, a digital signal offered better image quality compared to analog
technology. However, analog signal processing technology has improved
over the years and the difference in quality is now minimal.
c. Parallel Port – Most often used to connect a printer to the computer.
25-pin connector. Long and skinny, often pink in color. Transmits
data at 50-100 Kb/s.
d. USB Port – Universal Serial Bus. Now used to connect almost all
peripheral devices to the computer. USB 1.1 transmits data at 1.5 Mb/s
at low speed, 12 Mb/s at full speed. USB 2.0 transmits data at 480
Mb/s.
e. Firewire/ IEEE 1394 Port – Often found on Apple Computers. Often
used with digital camcorders. Firewire transmits data at 400 Mb/s.
Firewire 1394B (the new firewire) transmits data at 3.2 Gb/s.
f. PS/2 Port – sometimes called a mouse port, was developed by IBM. It
is used to connect a computer mouse or keyboard. Most computers
come with two PS/2 ports.
g. Ethernet Port – This port is used for networking and fast internet
connections. Data moves through them at speeds of either 10 megabits
or 100 megabits or 1 gigabit (1,000 megabits) depending on what
speed the network card in the computer supports. Little monitor lights
on these devices flicker when in use. - Power Supply – Gives your computer power by converting alternating
current (AC) supplied by the wall connection to direct current (DC). - Expansion Cards – Used to add/improve functionality to the computer.
a. Sound Card – Used to input and output sound under program control.
Sound cards provide better sound quality than the built in sound
control provided with most computers.
b. Graphics Card – Used to convert the logical representation of an
image to a signal that can be used as input for a monitor.
c. Network Card – Used to provide a computer connection over a
network. Transmit data at 10/100/1000 Mb/s. - CD ROM – A device used to read CD-ROMs. If capable of writing to the
CD-ROM, then they are usually referred to as a ‘burner’ or CD-RW. - DVD ROM – A device that is used to read DVDs/CDs. If capable of writing
to the DVD, then it is often referred to as a DVD-burner or a DVD-RW. - Floppy Drive – A device that is used to read/write to floppy diskettes.
- Fan – Keeps your computer cool. If the inside of your computer becomes too
hot, then the computer can overheat and damage parts. - Heatsink – Used to disperse the heat that is produced inside the computer by
the CPU and other parts by increasing surface area. - The little parts – Capacitors – store energy, Resistors – allows a current
through, Transistors – a valve which allows currents to be turned on or off. - Case – (Tower if standing upright.) What your motherboard, CPU, etc is
contained in.
The three main components of a computer: - CPU – Central Processing Unit, coordinates all actions that occur in the system,
executes program instructions. - Memory – Used to store information.
- I/O Devices – Input/Output devices, which allow you to obtain or display data.

This is very helpful sir
nice
This is very helpful thanks for this
Very informative. Please try to give more detailed information about hardware.
ok i give you more detailed information about hardware.
very informative knowledge for computer hardware,